Note
This article draws upon insights from my pro bono consulting work (2024–2025) on the “India Energy Stack,” a vision and framework I conceptualized and coined for the Smart Grid Observatory (SGO) of FSR Global. Although the concept was later released publicly without attribution, the ideas presented here reflect my original contribution.
India Energy Stack, a digital platform transforming India’s energy landscape and paving the way for a sustainable future.
Overview
India’s energy sector is at a critical juncture. With rising demand, rapid urbanization, and an accelerated push toward renewable energy, India must modernize its energy infrastructure to meet future challenges. The India Energy Stack (IES) is envisioned as a nationally shared digital public good that provides a standardized, modular, and secure digital framework to manage, monitor, and innovate across the energy ecosystem. IES integrates advanced data exchange protocols, real-time analytics, and open APIs to empower utilities, renewable energy producers, consumers, and innovators alike. By enabling seamless interoperability and ensuring robust privacy and security, the IES is poised to drive India’s transition to a sustainable, resilient, and smart energy future.
Introduction
India’s energy landscape is rapidly evolving. The twin challenges of ensuring energy access to millions while transitioning to cleaner, more sustainable sources require a reimagined digital infrastructure. Traditionally, data silos, fragmented systems, and disparate protocols have hampered cohesive decision-making and innovation in the energy sector. Recognizing these challenges, the India Energy Stack (IES) is designed to serve as a unifying digital platform that leverages modern data architectures, open standards, and modular microservices.
Inspired by the core principles of India’s existing Digital Public Infrastructures (DPIs), the India Energy Stack (IES) follows a layered approach tailored to the specific needs of energy management. By leveraging established digital public goods from the India Stack—such as Aadhaar for identity verification, secure digital payments, and consent frameworks—IES fosters a trusted data exchange ecosystem and enables collaborative innovation in energy services.
Guiding Design Principles
What makes the IES vision truly revolutionary is its layered approach that borrows from modern tech architecture:
To address the multifaceted challenges of the energy ecosystem, the IES is underpinned by several key design principles:
- Ecosystem Driven: The IES promotes collaboration among all stakeholders—including DISCOMs, renewable energy providers, consumers, regulators, and technology innovators—ensuring that solutions are tailored to the dynamic needs of India’s energy sector.
- Interoperability through Open APIs and Standards: By adopting open, vendor-neutral APIs and global energy standards, the IES facilitates seamless data exchange between diverse systems, enabling integration across smart grids, distributed renewable energy resources (DERs), and electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure.
- Privacy and Security by Design: Robust cybersecurity measures, data encryption, and consent-based data sharing (integrated with Aadhaar and DEPA frameworks) form the cornerstone of the IES, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure while empowering consumers with control over their data.
- Scalable and Evolvable Architecture: The IES is designed to handle millions of devices and trillions of data points, offering a modular architecture that can easily scale horizontally as new technologies and energy sources emerge.
- Unbundled and Modular: Embracing a micro services approach, the IES decomposes complex energy management challenges into independent, reusable modules. This unbundling enhances flexibility, enabling stakeholders to customize and extend solutions without reinventing the wheel.
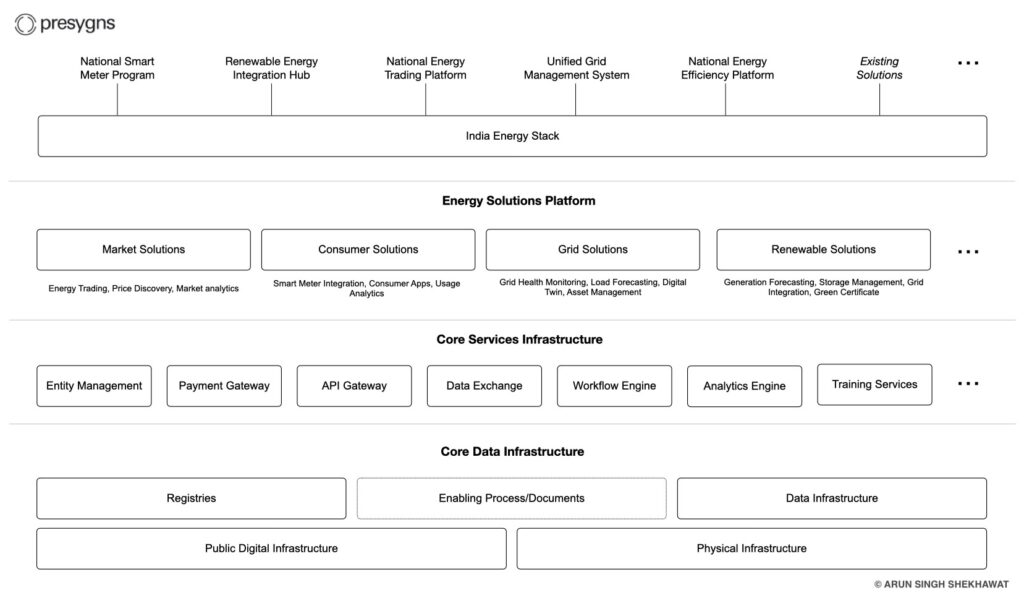
Architecture and Core Components
The IES is structured as a layered architecture comprising three core layers: the Core Data Infrastructure, the Core Services, and the Solutions & Innovation Platform.
Core Data Infrastructure Layer
This foundational layer establishes the “root of trust” through standardized electronic registries and robust data exchange protocols.
Registries
- Energy Identity Registry: Establishes unique digital identities for all energy-related entities, including consumers, producers, and grid assets.
- Utility Registry: Catalogs information on DISCOMs, energy providers, and their service areas to facilitate seamless inter-organizational collaboration.
- Renewable Asset Registry: Maintains a comprehensive database of distributed energy resources such as rooftop solar systems, wind turbines, EV charging stations, and mini-grids.
- Consumer Registry: Tracks energy consumption patterns, billing history, subsidy eligibility, and service quality metrics.
Data Infrastructure
Data Infrastructure layer in IES establishes a secure, scalable framework for managing and leveraging energy data. The platform supports:
- Comprehensive Data Categorization: Organizes energy data into Master, Transaction, Stream, and Derived types to support all aspects of energy management.
- Modular Micro services Architecture: Utilizes secure APIs and micro services to enable efficient data ingestion, processing, and customizable analytics.
- Robust Privacy and Security: Implements data anonymization, encryption, consent frameworks, and secure data enclaves to safeguard sensitive information.
- Trusted Data Sharing: Supports open data access and regulated data exchange via Data Exchange Fiduciaries, fostering collaboration and innovation in energy services.
- Real-Time Telemetry: Integration of smart meters, IoT sensors, and grid monitoring devices to capture live data.
- Consent-Based Sharing: Mechanisms that allow consumers to authorize data sharing with third parties while preserving privacy.
- Standardized Protocols: Uniform data formats and exchange standards to enable interoperability across diverse systems and stakeholders.
Core Services
The Core Services Layer delivers context-neutral, reusable micro services that power day-to-day energy operations and analytics. A few examples of core services:
- Entity Management: Manages core energy entity data—including consumers, producers, and assets—while ensuring secure user profile administration.
- Payment Gateway: Enables seamless digital transactions for energy billing and subsidy disbursement through integrated national payment systems.
- API Gateway: Offers a unified, secure interface for standardized API access, ensuring smooth integration across all energy services.
- Data Exchange: Facilitates real-time, secure data sharing between stakeholders using standardized protocols for trusted information flow.
- Workflow Engine: Automates energy operations and processes, streamlining task management, approvals, and service coordination.
- Analytics Engine: Provides advanced data insights and predictive analytics to optimize energy consumption, grid performance, and renewable integration.
- Training Services: Delivers standardized training modules and resources to upskill stakeholders in managing modern energy systems efficiently.
Solutions Platform
This top layer hosts a suite of context-aware, reusable services (APIs), tools, and libraries that build upon the Core Data Infrastructure and Core Services layers. A few examples of building blocks:
Market Solutions
- Energy Trading & Price Discovery: Solutions that enables peer-to-peer energy trading, automated price discovery, and settlement, facilitating efficient energy transactions.
- Market Analytics: Tools that analyze real-time demand-supply dynamics and pricing trends, empowering market participants with actionable insights.
Consumer Solutions
- Smart Meter Integration & Consumer Apps: Integrated solutions for seamless connectivity with smart meters, providing user-friendly interfaces for monitoring consumption and managing billing.
- Usage Analytics: Personalized dashboards and analytics that help consumers track energy consumption patterns and optimize efficiency.
Grid Solutions
- Grid Health Monitoring & Load Forecasting: Real-time monitoring systems that track grid performance and employ predictive analytics to forecast load demands and pre-empt outages.
- Digital Twin & Asset Management: Virtual models of grid operations that support scenario planning and efficient management of infrastructure assets throughout their lifecycle.
Renewable Solutions
- Generation Forecasting & Storage Management: Advanced forecasting tools for renewable energy generation paired with integrated systems to manage storage assets and balance grid demand.
- Grid Integration & Green Certificate Platforms: Solutions that streamline the integration of renewable sources into the grid while enabling the issuance and trading of green certificates to promote sustainability.
By leveraging these modular solutions, the IES not only addresses current energy challenges but also lays the groundwork for future innovations. Each solution is designed to be adaptable and extendable, ensuring that new energy programs can be rapidly developed using these proven building blocks.
Standards, Specifications, and Certification
To ensure interoperability, quality, and security, the IES will adhere to rigorous standards and certification processes:
- Open Standards and APIs: The IES leverages global energy data standards and open interfaces to promote vendor neutrality and interoperability among diverse stakeholders.
- Cybersecurity and Data Privacy: Compliance with national cybersecurity guidelines (e.g., CERT-In, MeitY) ensures robust protection for all digital assets. Encryption, consent-based data access, and secure data enclaves guarantee the privacy and integrity of sensitive information.
- Digital Twin and Simulation Models: Advanced simulation tools (digital twins) provide real-time grid monitoring and planning capabilities, enabling stakeholders to test and validate new solutions in a virtual environment before field deployment.
- Certification Programs: A structured certification process will validate the compliance of energy assets, systems, and service providers with established technical and security benchmarks, fostering trust and accountability across the ecosystem.
Governance and Ecosystem Enablement
The successful implementation of the IES depends on strong governance and an inclusive ecosystem approach:
- Federated Governance Model: A federated architecture empowers national and local agencies alike. Key stakeholders—including the Ministry of Power, Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC), Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), and state DISCOMs—will collaborate under a common governance framework, ensuring both central coordination and local agency.
- Multi-Channel Access and Inclusivity: Recognizing the diversity of users, the IES supports multiple access channels, including mobile applications, web platforms, SMS services, and community centers. This ensures that even digitally excluded communities can participate in and benefit from energy innovations.
- Public–Private Partnerships and Innovation Sandboxes: The IES fosters collaboration between government bodies, industry players, startups, research institutions, and accelerators. Innovation sandboxes will be established to encourage experimentation and rapid prototyping of new energy solutions.
- Regulatory and Policy Integration: Data-driven insights from the IES will inform policy formulation, regulatory oversight, and subsidy management, enhancing transparency and accountability in the energy sector.
Key Use Cases and Impact
The India Energy Stack is designed to address a wide array of critical use cases:
Smart Grids and Distributed Energy Management
- Real-Time Grid Monitoring: Enhances load balancing, predictive outage management, and efficient integration of renewable energy sources.
- Virtual Power Plant (VPP): Aggregates distributed generation to support grid stability during peak demand.
Consumer Empowerment
- Dynamic Pricing and Energy Budgeting: Real-time analytics and personalized energy dashboards empower consumers to optimize usage and reduce costs.
- Subsidy Management: Seamlessly links with Aadhaar and government databases to ensure that subsidies and financial incentives are accurately targeted and efficiently disbursed.
Policy, Regulation, and Sustainability
- Data-Driven Policy Formulation: Transparent, real-time data allows policymakers to design evidence-based interventions for energy efficiency and carbon reduction.
- Carbon Credit and Sustainability Marketplace: Facilitates the trade of renewable energy certificates (RECs) and carbon credits, incentivizing sustainable practices across the industry.
Innovation and Market Expansion
- Startup Ecosystem Enablement: Open APIs and data sandboxes lower the barriers to entry for innovators, fostering an environment of continuous improvement and technological advancement.
- Renewable Energy Marketplace: Promotes peer-to-peer energy trading and monetization of excess renewable generation, expanding market opportunities for distributed energy producers.
Future Roadmap
The India Energy Stack represents a transformative step toward a sustainable, resilient, and digitally enabled energy future. Over the coming years, the roadmap for IES will focus on:
- Scaling and Integration: Expanding the infrastructure to cover all regions, integrating more energy assets, and continuously updating data standards to accommodate emerging technologies.
- Enhancing Analytics and AI Capabilities: Leveraging advanced machine learning and AI to refine demand forecasting, grid management, and sustainability tracking, thereby driving further efficiencies.
- Deepening Ecosystem Collaboration: Strengthening public–private partnerships, expanding innovation hubs, and continually refining certification processes to build a robust, trusted, and agile energy ecosystem.
- Supporting India’s Net-Zero Ambitions: Directly contributing to national targets for renewable energy adoption and carbon neutrality, ensuring that India not only meets but exceeds its climate commitments.
In conclusion, the India Energy Stack is more than just a digital infrastructure—it is a catalyst for energy transformation. By unifying disparate systems, enabling data-driven decision making, and fostering innovation at all levels, IES will play a pivotal role in securing India’s energy future. The collaborative efforts of government, industry, and civil society will ensure that the IES evolves into a robust, scalable, and inclusive platform, driving India towards a cleaner, more efficient, and sustainable energy landscape.